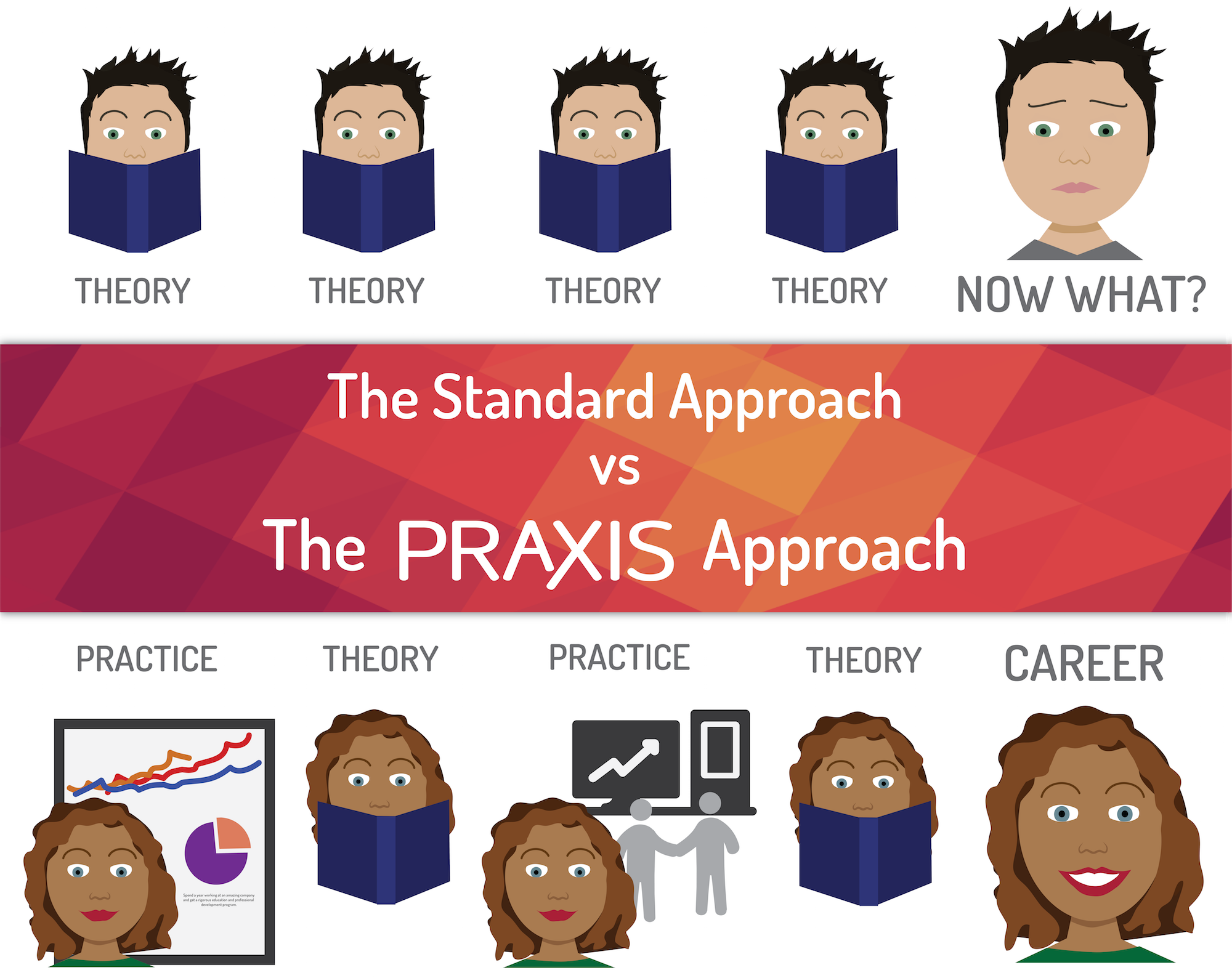
The same way you do everything else well. Practice, then reflect, then practice some more.
The common, conveyor-belt education system has a pretty bizarre approach to learning. It doesn’t mirror any learning pattern that high performers in any field use. It looks something like this:
Theory–>Theory–>Theory–>Theory–>Theory–>Practice (end)
In other words, you sit in classrooms studying things and memorizing knowledge from “experts” for nearly two decades. Then you’re supposed to take all that theory and successfully practice it in the real world and live happily ever after. Education is done, now you just go live well. You’re supposed to succeed in the marketplace and life after only ever thinking about it. Unless the theory is the practice – unless you’re learning to be an academic – this is a very bad way to learn.
I’ve written before about how absurd it would be if we taught bike riding the way we teach careers. But I’ve been thinking a lot lately about an even better comparison, and one I know more about than biking. Basketball.
How do you learn to play basketball?
First, you practice. Maybe on a mini hoop, maybe on a full-sized hoop. But you just start shooting and dribbling. After you have the basic motions and movements and muscle memory down, you start playing with other people in actual games. You play a lot of pick-up basketball. Maybe you play in an organized team setting. The coach might have you focus on specific aspects of the game or skills as you drill and condition. You’ll scrimmage, run plays, and plot your approach to offense and defense. You play, then a new concept is introduced, and you immediately play some more and try it out. Then you stop to reflect and get feedback, tweak your approach, and play again.
At the highest level, this pattern is even more pronounced. Good players practice a lot. There is no world in which merely theorizing about basketball teaches you to succeed on the court. Practice is always the first step and vastly more important if you have to choose one. But when you go from good to great players, something else happens. Theory comes into play. The learning pattern for playing most successfully looks something like this:
Practice–>Practice–>Theory–>Practice–>Practice–>Theory…(ad infinitum)
Great players spend more hours in the gym than anyone. But after they play they also reflect on their performance. They review film from previous games. They study what the offense did. They observe what happened and theorize about why they were stopped in the paint by this or that defense. They plan for the next game. They review film of the next opponent and plot an approach to match. They constantly reflect on the feedback they get from the real world of practice and play. They seek out other achievers who have struggled with mental toughness, or strength building, or recovery from injury. They employ motivational tactics and specialized training.
Notice the pattern because it’s very important. Hours of film study and offensive scheming are of no value to the novice. If you’ve never hoisted a ball in the air, learning the perfect placement of your index finger or the optimal use of trash-talk to gain a mental edge isn’t going to help you. Theory is hugely important. But it becomes important only when it has past practice upon which to reflect and future practice for which to prepare.
Notice also that, unlike the conveyor-belt education system, the basketball model is never done. There is no end point. It’s an ongoing process. There is no graduation. Michael Jordan, at the peak of his game and dominating the greatest ballers on the planet, famously came back from every offseason with something new. He practiced. He reflected and theorized. He tested it with more practice.
In this model the role of teacher fades almost entirely. Specialists with knowledge of the history of the game or the mechanics of the human elbow can be employed in specific situations when needed, but they are in no way the key ingredient to learning the game nor are they valuably employed until a whole lot of playing has occurred. Instead, coaches and trainers emerge. People who don’t tell you which facts about basketball are correct and must be memorized, but people who challenge you to get off your butt when you don’t feel like practicing. People who help you in the process of reflecting on your unique game and keep you accountable to your unique practice process. They are observers who watch you in the actual act of playing the game and provide real-time feedback from their vantage point. They aren’t your authority – you can find a new coach anytime – but there for motivation and insight. Some of the greatest players are famous for ignoring their coaches as often as listening to them even though they deeply respect them, which strikes me as a pretty normal and healthy way to see the relationship.
Another important thing about learning basketball is the value of mimicry. How did the hook shot join the common arsenal of post players? Because someone did it well and everyone who played against them realized how effective it could be and began to copy it. How do you learn to crossover or headfake? By being crossedover or headfaked at the playground and determining to do the same.
Learning happens more from being around people and environments than it does from consciously thinking about them. You have to be immersed in the actual play of the game.
My friend and colleague at Praxis – TK Coleman, our Education Director – loves the game of basketball probably even more than I do. We don’t view this analogy as just a cute comparison. I think success in any career is far more like success in basketball than it is like success in a classroom. The principles of learning the game are the principles of learning to perform in just about every other arena. This is why we are so focused on apprenticing at startups and small businesses – practice – and reflecting on the experience and how new skills and mindsets can make it better – theory – and trying them out – practice – and discussing…etc. This is why our advisers have coaching sessions with participants, rather than giving them lectures. Philosophy is hugely important to success in any field. But only if you’re already in the field trying things out.
Kids aren’t practicing for life or career by sitting in the classroom taking tests. They’re theorizing about it. They’re not observing those who are successful (except, best case, at teaching) and mimicking them. They’re reading what other people said about the successful. They’re being introduced to a few fragments of the history of the game or uniform design or what one conditioning coach thinks about one approach to calf muscles. They’re not being transformed into great players, they’re simply checking the memorization of lifeless, contextless knowledge off a list of assignments.
You can’t expect to win by studying. You’ve got to play the game.
Like this:
Like Loading...